Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
OpenDocCN
sklearn-doc-zh
提交
26ce19f4
S
sklearn-doc-zh
项目概览
OpenDocCN
/
sklearn-doc-zh
通知
3
Star
3
Fork
0
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
0
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
S
sklearn-doc-zh
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
0
Issue
0
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
合并请求
0
Pages
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
提交
Issue看板
前往新版Gitcode,体验更适合开发者的 AI 搜索 >>
未验证
提交
26ce19f4
编写于
4月 02, 2020
作者:
N
N!no
提交者:
GitHub
4月 02, 2020
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
差异文件
Merge pull request #414 from LovelyBuggies/master
nino-patch-examples-bicluster intepretion
上级
27c6f70a
964da177
变更
5
隐藏空白更改
内联
并排
Showing
5 changed file
with
323 addition
and
5 deletion
+323
-5
docs/examples/Biclustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_clustering_algorithm.md
...clustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_clustering_algorithm.md
+78
-0
docs/examples/Biclustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md
...stering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md
+66
-0
docs/examples/Biclustering/biclustering_documents_with_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md
...ng_documents_with_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md
+174
-0
docs/examples/README.md
docs/examples/README.md
+3
-3
docs/examples/SUMMARY.md
docs/examples/SUMMARY.md
+2
-2
未找到文件。
docs/examples/Biclustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_clustering_algorithm.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
26ce19f4
# 频谱双聚类算法的演示
> 翻译者:[@N!no](https://github.com/lovelybuggies)
> 校验者:待校验
这个例子演示了如何使用光谱聚类算法生成棋盘数据集并对其进行聚类处理。
数据是用
`make_checkerboard`
函数生成的,然后打乱顺序并传递给光谱双聚类算法。变换后的矩阵的行和列被重新排列,以显示该算法找到的双聚类。
行和列标签向量的外积表示棋盘结构。
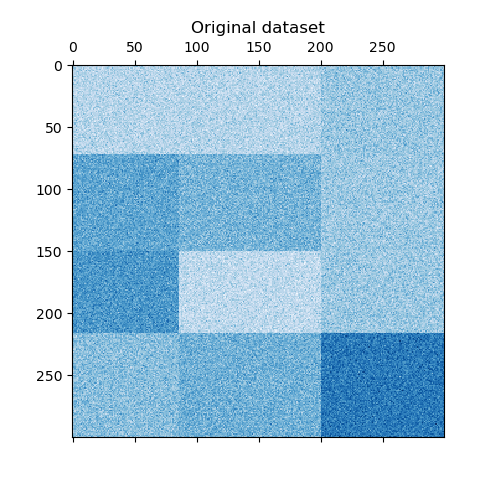
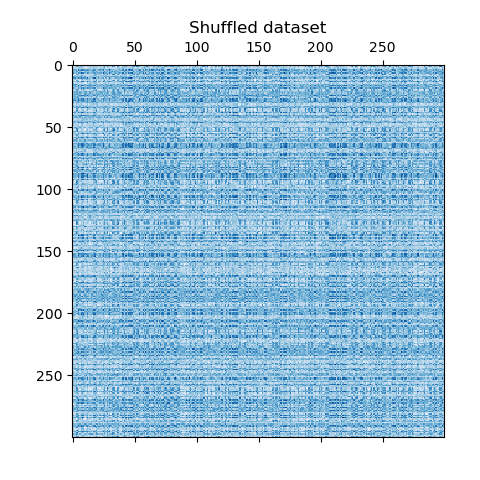
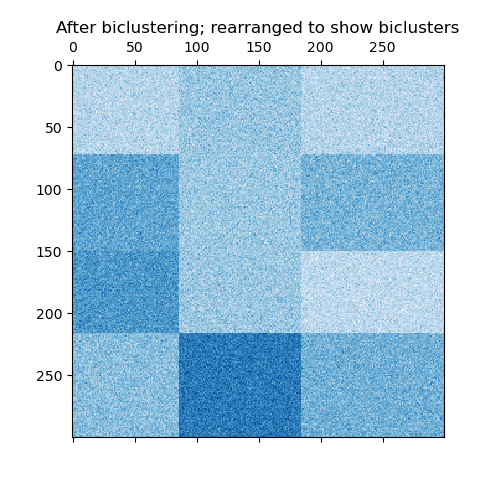
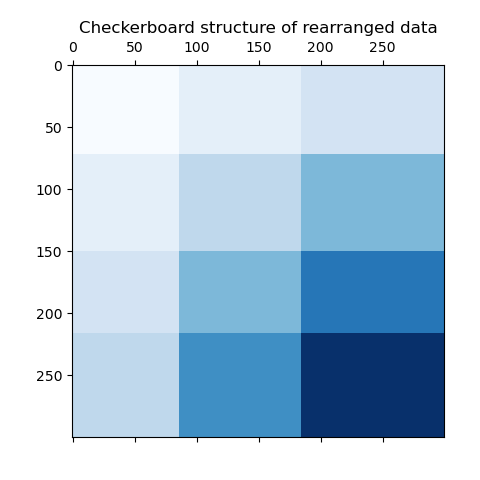
```
consensus score: 1.0
```
```
python
print
(
__doc__
)
# Author: Kemal Eren <kemal@kemaleren.com>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import
numpy
as
np
from
matplotlib
import
pyplot
as
plt
from
sklearn.datasets
import
make_checkerboard
from
sklearn.cluster
import
SpectralBiclustering
from
sklearn.metrics
import
consensus_score
n_clusters
=
(
4
,
3
)
data
,
rows
,
columns
=
make_checkerboard
(
shape
=
(
300
,
300
),
n_clusters
=
n_clusters
,
noise
=
10
,
shuffle
=
False
,
random_state
=
0
)
plt
.
matshow
(
data
,
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"Original dataset"
)
# 打乱聚类顺序
rng
=
np
.
random
.
RandomState
(
0
)
row_idx
=
rng
.
permutation
(
data
.
shape
[
0
])
col_idx
=
rng
.
permutation
(
data
.
shape
[
1
])
data
=
data
[
row_idx
][:,
col_idx
]
plt
.
matshow
(
data
,
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"Shuffled dataset"
)
model
=
SpectralBiclustering
(
n_clusters
=
n_clusters
,
method
=
'log'
,
random_state
=
0
)
model
.
fit
(
data
)
score
=
consensus_score
(
model
.
biclusters_
,
(
rows
[:,
row_idx
],
columns
[:,
col_idx
]))
print
(
"consensus score: {:.1f}"
.
format
(
score
))
fit_data
=
data
[
np
.
argsort
(
model
.
row_labels_
)]
fit_data
=
fit_data
[:,
np
.
argsort
(
model
.
column_labels_
)]
plt
.
matshow
(
fit_data
,
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"After biclustering; rearranged to show biclusters"
)
plt
.
matshow
(
np
.
outer
(
np
.
sort
(
model
.
row_labels_
)
+
1
,
np
.
sort
(
model
.
column_labels_
)
+
1
),
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"Checkerboard structure of rearranged data"
)
plt
.
show
()
```
docs/examples/Biclustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
26ce19f4
# 频谱共聚算法演示
> 翻译者:[@N!no](https://github.com/lovelybuggies)
> 校验者:待校验
这个例子演示了如何使用谱协聚类算法生成数据集并对其进行双聚类处理。
数据集是使用
`make_biclusters`
函数生成的,该函数创建一个小值矩阵,并将大值植入双聚类。然后将行和列打乱并传递给光谱协聚算法。通过重新排列变换后的矩阵可以使双聚类连续,这展示出该算法找到双聚类的准确性。
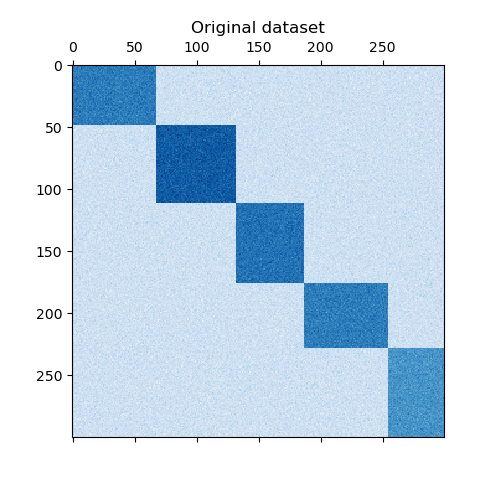
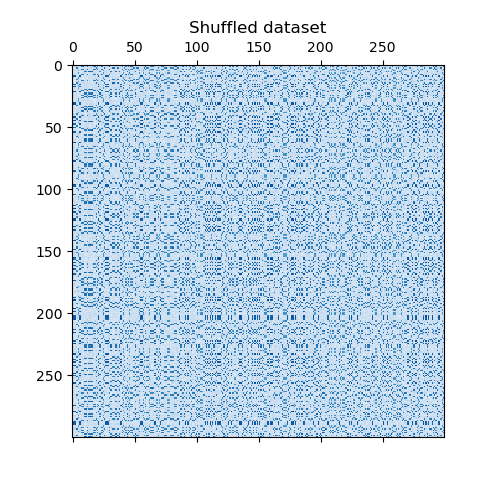
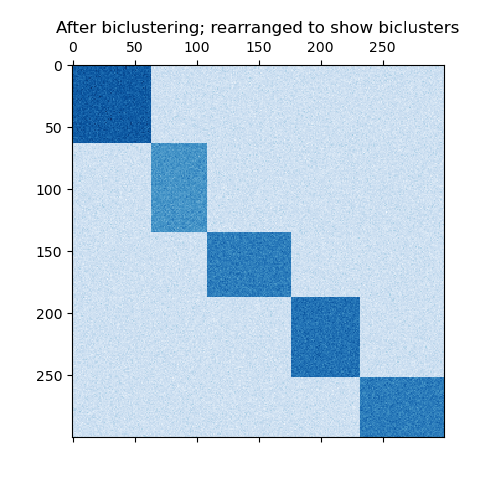
```
consensus score: 1.0
```
```
python
print
(
__doc__
)
# Author: Kemal Eren <kemal@kemaleren.com>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import
numpy
as
np
from
matplotlib
import
pyplot
as
plt
from
sklearn.datasets
import
make_biclusters
from
sklearn.cluster
import
SpectralCoclustering
from
sklearn.metrics
import
consensus_score
data
,
rows
,
columns
=
make_biclusters
(
shape
=
(
300
,
300
),
n_clusters
=
5
,
noise
=
5
,
shuffle
=
False
,
random_state
=
0
)
plt
.
matshow
(
data
,
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"Original dataset"
)
# 打乱聚类的位置
rng
=
np
.
random
.
RandomState
(
0
)
row_idx
=
rng
.
permutation
(
data
.
shape
[
0
])
col_idx
=
rng
.
permutation
(
data
.
shape
[
1
])
data
=
data
[
row_idx
][:,
col_idx
]
plt
.
matshow
(
data
,
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"Shuffled dataset"
)
model
=
SpectralCoclustering
(
n_clusters
=
5
,
random_state
=
0
)
model
.
fit
(
data
)
score
=
consensus_score
(
model
.
biclusters_
,
(
rows
[:,
row_idx
],
columns
[:,
col_idx
]))
print
(
"consensus score: {:.3f}"
.
format
(
score
))
fit_data
=
data
[
np
.
argsort
(
model
.
row_labels_
)]
fit_data
=
fit_data
[:,
np
.
argsort
(
model
.
column_labels_
)]
plt
.
matshow
(
fit_data
,
cmap
=
plt
.
cm
.
Blues
)
plt
.
title
(
"After biclustering; rearranged to show biclusters"
)
plt
.
show
()
```
docs/examples/Biclustering/biclustering_documents_with_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
26ce19f4
# 使用频谱共聚算法对文档进行聚合
> 翻译者:[@N!no](https://github.com/lovelybuggies)
> 校验者:待校验
这个例子演示了20个新闻组数据集上的光谱协聚类算法。‘comp.os.ms-windows.misc’ 类别被排除在外,因为它包含许多只包含数据的帖子。
TF-IDF 矢量帖构成一个词频矩阵,然后使用 Dhillon 光谱协聚算法对其进行重组。由此产生的文档词双聚类表明在这些子集文档中被使用频率更高的子集词。
对于一些最好的双聚类来说,它最常见的文档类别和十个最重要的单词会被打印出来。最佳双类别由其归一化的切割决定。最好的单词是通过比较它们在两区内和两区外的总和来确定的。
为了进行比较,我们还使用 MiniBatchKMeans 对文档进行集群。从双聚类衍生出的文档聚类比使用 MiniBatchKMeans 得到的聚类具有更好的 V-measure。
```
Vectorizing...
Coclustering...
Done in 2.75s. V-measure: 0.4387
MiniBatchKMeans...
Done in 5.69s. V-measure: 0.3344
Best biclusters:
----------------
bicluster 0 : 1829 documents, 2524 words
categories : 22% comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware, 19% comp.sys.mac.hardware, 18% comp.graphics
words : card, pc, ram, drive, bus, mac, motherboard, port, windows, floppy
bicluster 1 : 2391 documents, 3275 words
categories : 18% rec.motorcycles, 17% rec.autos, 15% sci.electronics
words : bike, engine, car, dod, bmw, honda, oil, motorcycle, behanna, ysu
bicluster 2 : 1887 documents, 4232 words
categories : 23% talk.politics.guns, 19% talk.politics.misc, 13% sci.med
words : gun, guns, firearms, geb, drugs, banks, dyer, amendment, clinton, cdt
bicluster 3 : 1146 documents, 3263 words
categories : 29% talk.politics.mideast, 26% soc.religion.christian, 25% alt.atheism
words : god, jesus, christians, atheists, kent, sin, morality, belief, resurrection, marriage
bicluster 4 : 1732 documents, 3967 words
categories : 26% sci.crypt, 23% sci.space, 17% sci.med
words : clipper, encryption, key, escrow, nsa, crypto, keys, intercon, secure, wiretap
```
```
python
from
collections
import
defaultdict
import
operator
from
time
import
time
import
numpy
as
np
from
sklearn.cluster
import
SpectralCoclustering
from
sklearn.cluster
import
MiniBatchKMeans
from
sklearn.datasets
import
fetch_20newsgroups
from
sklearn.feature_extraction.text
import
TfidfVectorizer
from
sklearn.metrics.cluster
import
v_measure_score
print
(
__doc__
)
def
number_normalizer
(
tokens
):
""" 将所有数字标记映射到占位符。
对于许多应用程序来说,以数字开头的令牌并没有直接的用处,但是这样的令牌存在的事实可能是相关的。通过应用这种降维形式,一些方法可能会表现得更好。
"""
return
(
"#NUMBER"
if
token
[
0
].
isdigit
()
else
token
for
token
in
tokens
)
class
NumberNormalizingVectorizer
(
TfidfVectorizer
):
def
build_tokenizer
(
self
):
tokenize
=
super
().
build_tokenizer
()
return
lambda
doc
:
list
(
number_normalizer
(
tokenize
(
doc
)))
# 不包含 'comp.os.ms-windows.misc' 类别
categories
=
[
'alt.atheism'
,
'comp.graphics'
,
'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware'
,
'comp.sys.mac.hardware'
,
'comp.windows.x'
,
'misc.forsale'
,
'rec.autos'
,
'rec.motorcycles'
,
'rec.sport.baseball'
,
'rec.sport.hockey'
,
'sci.crypt'
,
'sci.electronics'
,
'sci.med'
,
'sci.space'
,
'soc.religion.christian'
,
'talk.politics.guns'
,
'talk.politics.mideast'
,
'talk.politics.misc'
,
'talk.religion.misc'
]
newsgroups
=
fetch_20newsgroups
(
categories
=
categories
)
y_true
=
newsgroups
.
target
vectorizer
=
NumberNormalizingVectorizer
(
stop_words
=
'english'
,
min_df
=
5
)
cocluster
=
SpectralCoclustering
(
n_clusters
=
len
(
categories
),
svd_method
=
'arpack'
,
random_state
=
0
)
kmeans
=
MiniBatchKMeans
(
n_clusters
=
len
(
categories
),
batch_size
=
20000
,
random_state
=
0
)
print
(
"Vectorizing..."
)
X
=
vectorizer
.
fit_transform
(
newsgroups
.
data
)
print
(
"Coclustering..."
)
start_time
=
time
()
cocluster
.
fit
(
X
)
y_cocluster
=
cocluster
.
row_labels_
print
(
"Done in {:.2f}s. V-measure: {:.4f}"
.
format
(
time
()
-
start_time
,
v_measure_score
(
y_cocluster
,
y_true
)))
print
(
"MiniBatchKMeans..."
)
start_time
=
time
()
y_kmeans
=
kmeans
.
fit_predict
(
X
)
print
(
"Done in {:.2f}s. V-measure: {:.4f}"
.
format
(
time
()
-
start_time
,
v_measure_score
(
y_kmeans
,
y_true
)))
feature_names
=
vectorizer
.
get_feature_names
()
document_names
=
list
(
newsgroups
.
target_names
[
i
]
for
i
in
newsgroups
.
target
)
def
bicluster_ncut
(
i
):
rows
,
cols
=
cocluster
.
get_indices
(
i
)
if
not
(
np
.
any
(
rows
)
and
np
.
any
(
cols
)):
import
sys
return
sys
.
float_info
.
max
row_complement
=
np
.
nonzero
(
np
.
logical_not
(
cocluster
.
rows_
[
i
]))[
0
]
col_complement
=
np
.
nonzero
(
np
.
logical_not
(
cocluster
.
columns_
[
i
]))[
0
]
# 注意:接下来的操作等同于 X[rows[:, np.newaxis], cols].sum()
# 但是会针对于 scipy <= 0.16 的版本更快一些
weight
=
X
[
rows
][:,
cols
].
sum
()
cut
=
(
X
[
row_complement
][:,
cols
].
sum
()
+
X
[
rows
][:,
col_complement
].
sum
())
return
cut
/
weight
def
most_common
(
d
):
"""默认字典有最大值的项。
在 Python >= 2.7 中类似于 Counter.most_common 。
"""
return
sorted
(
d
.
items
(),
key
=
operator
.
itemgetter
(
1
),
reverse
=
True
)
bicluster_ncuts
=
list
(
bicluster_ncut
(
i
)
for
i
in
range
(
len
(
newsgroups
.
target_names
)))
best_idx
=
np
.
argsort
(
bicluster_ncuts
)[:
5
]
print
()
print
(
"Best biclusters:"
)
print
(
"----------------"
)
for
idx
,
cluster
in
enumerate
(
best_idx
):
n_rows
,
n_cols
=
cocluster
.
get_shape
(
cluster
)
cluster_docs
,
cluster_words
=
cocluster
.
get_indices
(
cluster
)
if
not
len
(
cluster_docs
)
or
not
len
(
cluster_words
):
continue
# 种类
counter
=
defaultdict
(
int
)
for
i
in
cluster_docs
:
counter
[
document_names
[
i
]]
+=
1
cat_string
=
", "
.
join
(
"{:.0f}% {}"
.
format
(
float
(
c
)
/
n_rows
*
100
,
name
)
for
name
,
c
in
most_common
(
counter
)[:
3
])
# 单词
out_of_cluster_docs
=
cocluster
.
row_labels_
!=
cluster
out_of_cluster_docs
=
np
.
where
(
out_of_cluster_docs
)[
0
]
word_col
=
X
[:,
cluster_words
]
word_scores
=
np
.
array
(
word_col
[
cluster_docs
,
:].
sum
(
axis
=
0
)
-
word_col
[
out_of_cluster_docs
,
:].
sum
(
axis
=
0
))
word_scores
=
word_scores
.
ravel
()
important_words
=
list
(
feature_names
[
cluster_words
[
i
]]
for
i
in
word_scores
.
argsort
()[:
-
11
:
-
1
])
print
(
"bicluster {} : {} documents, {} words"
.
format
(
idx
,
n_rows
,
n_cols
))
print
(
"categories : {}"
.
format
(
cat_string
))
print
(
"words : {}
\n
"
.
format
(
', '
.
join
(
important_words
)))
```
docs/examples/README.md
浏览文件 @
26ce19f4
...
@@ -13,13 +13,13 @@ scikit-learn 的 Miscellaneous 和入门示例。
...
@@ -13,13 +13,13 @@ scikit-learn 的 Miscellaneous 和入门示例。
| !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_kernel_ridge_regression_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
内核岭回归和SVR的比较
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/plot_kernel_ridge_regression.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-plot-kernel-ridge-regression-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id10) | !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_kernel_approximation_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
RBF内核的显式特征图逼近
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/plot_kernel_approximation.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-plot-kernel-approximation-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id11) |
| !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_kernel_ridge_regression_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
内核岭回归和SVR的比较
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/plot_kernel_ridge_regression.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-plot-kernel-ridge-regression-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id10) | !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_kernel_approximation_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
RBF内核的显式特征图逼近
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/plot_kernel_approximation.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-plot-kernel-approximation-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id11) |
## 双
集群
## 双
聚类
有关
`sklearn.cluster.bicluster`
模块的示例。
有关
`sklearn.cluster.bicluster`
模块的示例。
| | | | |
| | | | |
| -- | -- | -- | -- |
| -- | -- | -- | -- |
| !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_spectral_coclustering_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
频谱共聚算法演示
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/bicluster/plot_spectral_coclustering.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-bicluster-plot-spectral-coclustering-py
)[]
(
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id12) | !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_spectral_biclustering_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
频谱二值化算法的演示
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/bicluster/plot_spectral_biclustering.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-bicluster-plot-spectral-biclustering-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id13) | !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_bicluster_newsgroups_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
使用频谱共同聚类算法对文档进行聚类
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/bicluster/plot_bicluster_newsgroups.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-bicluster-plot-bicluster-newsgroups-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id14)
|
| !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_spectral_coclustering_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
频谱共聚算法演示
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/bicluster/plot_spectral_coclustering.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-bicluster-plot-spectral-coclustering-py
)[]
(
Biclustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md) | !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_spectral_biclustering_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
频谱双聚类算法的演示
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/bicluster/plot_spectral_biclustering.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-bicluster-plot-spectral-biclustering-py
)[]
(Biclustering/a_demo_of_the_spectral_clustering_algorithm.md) | !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_bicluster_newsgroups_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
使用频谱共聚算法对文档进行聚合
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/bicluster/plot_bicluster_newsgroups.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-bicluster-plot-bicluster-newsgroups-py
)[]
(Biclustering/biclustering_documents_with_the_spectral_co-clustering_algorithm.md) |
|
## 校准
## 校准
...
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ scikit-learn 的 Miscellaneous 和入门示例。
...
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ scikit-learn 的 Miscellaneous 和入门示例。
| !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_lda_qda_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
线性和二次判别分析与协方差椭球
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-classification-plot-lda-qda-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id23) |
| !
[](
img/sphx_glr_plot_lda_qda_thumb.png
)
<br/>
[
线性和二次判别分析与协方差椭球
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-classification-plot-lda-qda-py
)[]
(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/index.html#id23) |
## 多
集群
## 多
聚类
有关
[
`sklearn.cluster`
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.cluster
"sklearn.cluster"
)
模块的示例。
有关
[
`sklearn.cluster`
](
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.cluster
"sklearn.cluster"
)
模块的示例。
...
...
docs/examples/SUMMARY.md
浏览文件 @
26ce19f4
*
其他示例
*
其他示例
*
双
集群
*
双
聚类
*
校准
*
校准
*
分类
*
分类
*
多
集群
*
多
聚类
*
协方差估计
*
协方差估计
*
交叉分解
*
交叉分解
*
数据集示例
*
数据集示例
...
...
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录