README.md
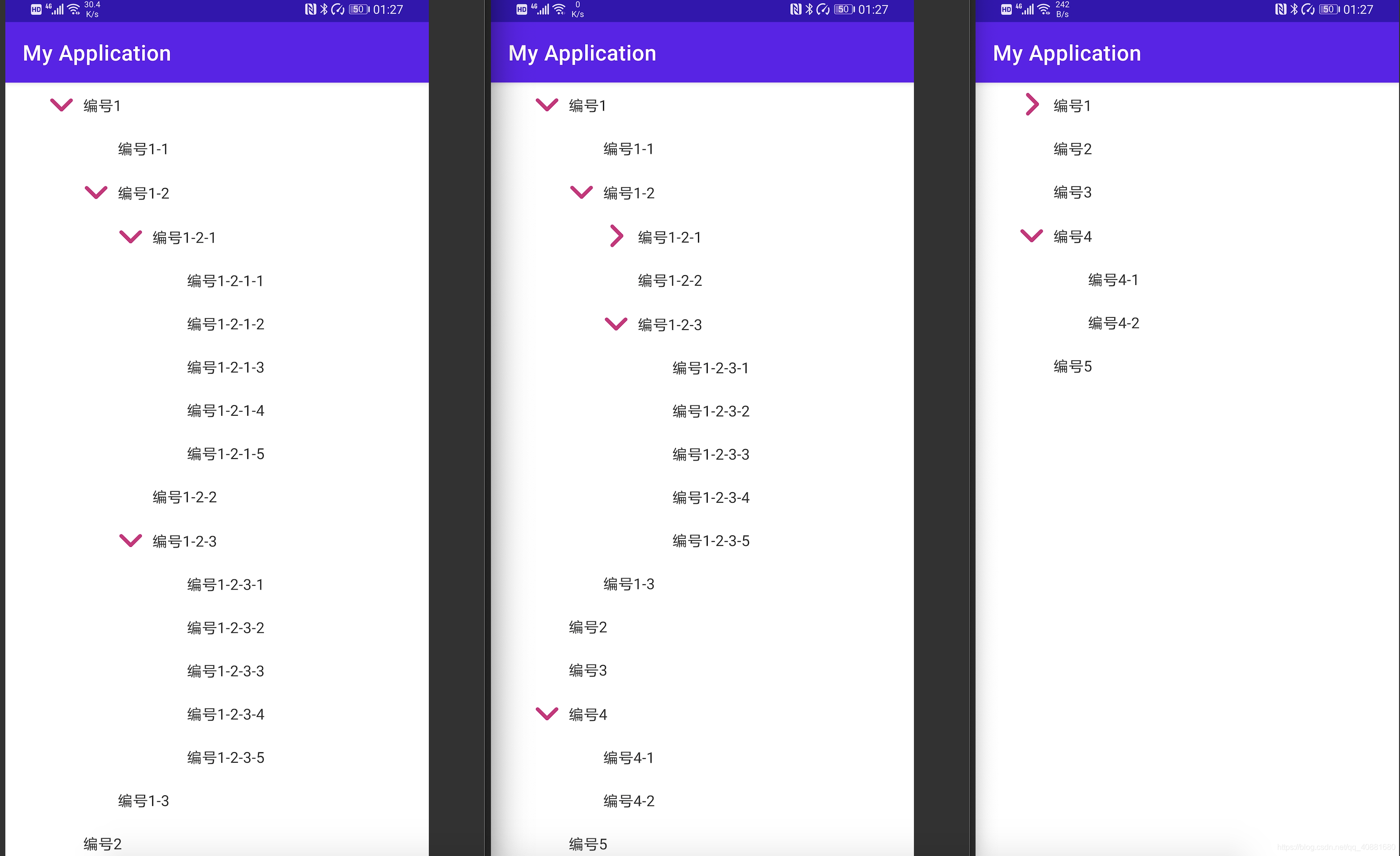
先上效果图
前言
前些天有个朋友问我,要实现一个树状的列表要怎么做,根据一个完全符合规则但是却很头疼的一个Json解析来实现,见下格式,对于有些Android开发者来说,这个Json或许并不友好,没有办法直接转成实体类,其实这一串Json解析映射成可折叠列表也并不难!
{
"code":"200",
"message":"success",
"data":[
{
"id":"1001",
"title":"编号1",
"next":[
{
"id":"10011",
"title":"编号1-1"
},
{
"id":"10012",
"title":"编号1-2",
"next":[
{
"id":"100121",
"title":"编号1-2-1",
"next":[
{
"id":"1001211",
"title":"编号1-2-1-1"
},
{
"id":"1001212",
"title":"编号1-2-1-2"
},
{
"id":"1001213",
"title":"编号1-2-1-3"
},
{
"id":"1001214",
"title":"编号1-2-1-4"
},
{
"id":"1001215",
"title":"编号1-2-1-5"
}
]
},
{
"id":"100122",
"title":"编号1-2-2"
},
{
"id":"100123",
"title":"编号1-2-3",
"next":[
{
"id":"1001231",
"title":"编号1-2-3-1"
},
{
"id":"1001232",
"title":"编号1-2-3-2"
},
{
"id":"1001233",
"title":"编号1-2-3-3"
},
{
"id":"1001234",
"title":"编号1-2-3-4"
},
{
"id":"1001235",
"title":"编号1-2-3-5"
}
]
}
]
},
{
"id":"10013",
"title":"编号1-3"
}
]
},
{
"id":"1002",
"title":"编号2"
},
{
"id":"1003",
"title":"编号3"
},
{
"id":"1004",
"title":"编号4",
"next":[
{
"id":"10041",
"title":"编号4-1"
},
{
"id":"10042",
"title":"编号4-2"
}
]
},
{
"id":"1005",
"title":"编号5"
}
]
}拿到这一串不确定层级的Json该想什么?用什么去解析?该用什么控件?
逐层addView方式
其实可以直接使用Gson解析,不过这个实体类要自己手写一下:
package com.example.myapplication;
import java.util.List;
public class DataBean {
private String code;
private String message;
private List<Data> data;
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public List<Data> getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(List<Data> data) {
this.data = data;
}
public static class Data {
private String id;
private String title;
private List<Data> next;//重点在这里
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public List<Data> getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(List<Data> next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
}
( OpenParam.json为那个json字符串 )
使用Gson解析:
Kotlin:
val dataBean = Gson().fromJson(OpenParam.json, DataBean().javaClass)Java:
DataBean dataBean = new Gson().fromJson(OpenParam.json, DataBean.class)既然解析出来了,之后可以通过递归来逐渐addView()的方式实现,判断next字段是否为null即可!但要在递归开始之前,先要分析一下布局!
既然要逐级嵌套,先来一个LinearLayout,当然这个列表是可滑动的,外层嵌套一个ScrollView即可,Activity布局那就是这样的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/treeLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>之后要分析每一个条目,有两种情况,一种是带子布局的item,一种是不带子布局的item,当遇到有嵌套的情况,即存在next字段,就可以使用带子布局的item,反之则是另一个!那么这两种布局就是如下:
带子布局的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/flag"
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="32dp"
android:padding="8dp"
android:src="@mipmap/open" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginTop="1dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingRight="32dp"
android:textColor="#333333" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/nextLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="32dp"
android:orientation="vertical" />
</LinearLayout>不带子布局的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="72dp"
android:layout_marginRight="32dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:textColor="#333333" />
</LinearLayout>之后便是根据实体类来递归实现,循环遍历,判断是否存在next字段而做出两种情况,如在37行到69行之间代码!存在子节点使用带有子布局的item,反之使用另一个!
package com.example.myapplication
import android.animation.ObjectAnimator
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.LayoutInflater.from
import android.view.View
import android.widget.LinearLayout
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.isGone
import com.google.gson.Gson
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.item_text.view.*
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.item_tree.view.*
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var objectAnimator: ObjectAnimator
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
//解析Json
val dataBean = Gson().fromJson(OpenParam.json, DataBean().javaClass)
//创建View
createView(dataBean.data, treeLayout)
}
/**
* 递归创建布局
*/
private fun createView(dataList: MutableList<DataBean.Data>, linearLayout: LinearLayout) {
for (i in 0 until dataList.size) {
val title = dataList[i].title
val next = dataList[i].next
if (null != next) {
val childLayout = from(this).inflate(R.layout.item_tree, null, false)
childLayout.title.text = title
//展开和关闭的点击事件
childLayout.title.setOnClickListener {
if (childLayout.nextLayout.isGone) {
//展开
childLayout.nextLayout.visibility = View.VISIBLE
//添点展开动画
objectAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(childLayout.flag, "rotation", 0f)
objectAnimator.duration = 400
objectAnimator.start()
} else {
//隐藏
childLayout.nextLayout.visibility = View.GONE
//添点关闭动画
objectAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(childLayout.flag, "rotation", -90f)
objectAnimator.duration = 400
objectAnimator.start()
}
}
createView(next, childLayout.nextLayout)
linearLayout.addView(childLayout)
} else {
val textLayout = from(this).inflate(R.layout.item_text, null, false)
textLayout.info.text = title
linearLayout.addView(textLayout)
}
}
}
}这样便实现了,这种适用于常规的折叠列表,如果遇到需要加载更多的情况下,可以直接判断ScrollView是否滚动到底部,并且上次的网络加载是否完成,达成条件则再次调用27行代码进行插入即可!这里不再多做解释,不懂的朋友可以直接评论区问我!