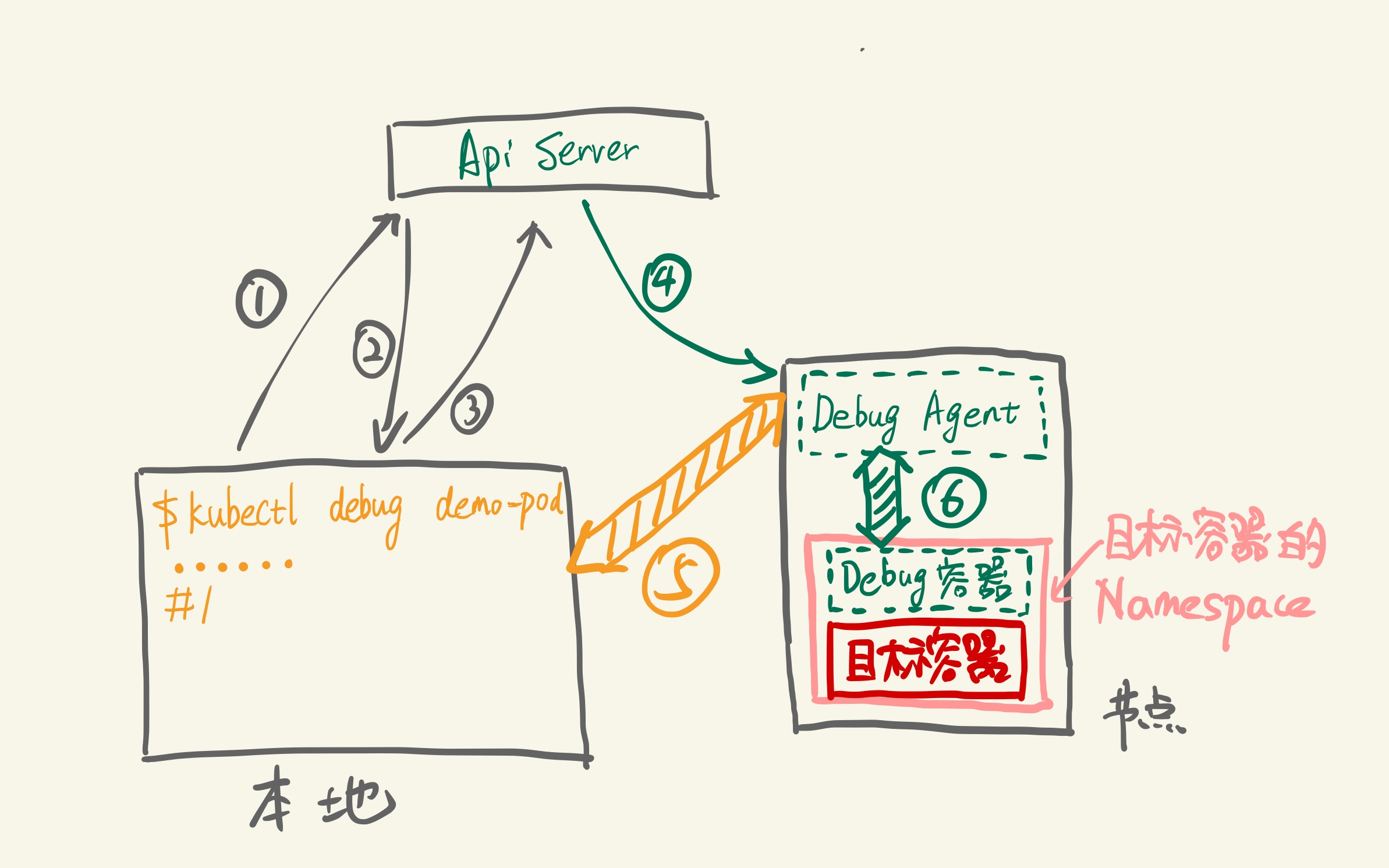
k8s debug
Showing
computer/RAID.md
0 → 100644
golang/bugs.md
0 → 100644
kubernetes/cdk8s.md
0 → 100644
kubernetes/img/kube-debug.gif
0 → 100644
2.0 MB
293.2 KB
linux/ssh.md
0 → 100644